- One semaphore for mutual exclusion on the state variables.
- One semaphore for each class of waiting; used just as a convenience to make a process wait. In the worst case, one semaphore per process.
Whenever possible, cast problems into the first class. This usually can be done.
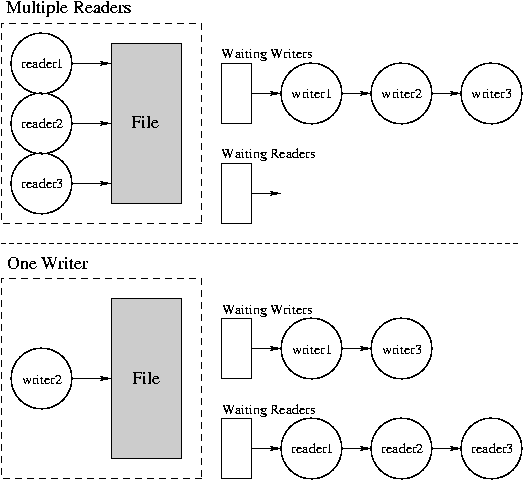
Unfortunately, sometimes a resource is shared by different classes of users; that is, they use the resource in different ways. Potentially the different kinds of usage interact. For example, consider a shared database with readers and writers. It is safe for any number of readers to access the database simultaneously, but each writer must have exclusive access. Example: checking account (statement-generators are readers, tellers are writers).
- Note that writers are actually readers too.
- In this case, the constraints are too complicated to be solved single-handedly with semaphores.
-
Constraints:
- Readers can only proceed if there are no active or waiting writers (use semaphore OKToRead).
- Writers can only proceed if there are no active readers or writers (use semaphore OKToWrite).
- Only one process may manipulate internal state variables at once (use semaphore Lock).
- Scheduling: writers get preference.
-
State variables:
- AR = number of active readers.
- WR = number of waiting readers.
- AW = number of active writers.
- WW = number of waiting writers.
AW is always 0 or 1. AR and AW may not both be non-zero.
-
Initialization:
- semaphore OKToRead (0);
- semaphore OKToWrite semaphore(0);
- semaphore Lock = semaphore(1);
- volatile int AR = 0, WR = 0, AW = 0, WW = 0;
| Reader Process: | Writer Process: |
|---|---|
StartRead ()
{
P(Lock);
if ((AW+WW) != 0) {
WR++;
V(Lock);
P(OKToRead);
} else {
AR++;
V(Lock);
}
}
|
StartWrite ()
{
P(Lock);
if ((AW+AR+WW) != 0) {
WW++;
V(Lock);
P(OKToWrite);
} else {
AW++;
V(Lock);
}
}
|
EndRead ()
{
P(Lock);
AR--;
if ((AR == 0) and (WW > 0)) {
V(OKToWrite);
AW++;
WW--;
}
V(Lock);
}
|
EndWrite ()
P(Lock);
AW--;
if (WW>0) {
V(OKToWrite);
AW++;
WW--;
} else {
while (WR>0) {
V(OKToRead);
AR++;
WR--;
}
}
V(Lock);
}
|
main ()
{
StartRead();
// --read the necessary data--
EndRead();
}
|
main ()
{
StartWrite();
// --write the necessary data--
EndWrite();
}
|
Examples:
- Reader enters and leaves system.
- Writer enters and leaves system.
- Two readers enter system.
- Writer enters system and waits.
- Reader enters system and waits.
- Readers leave system, writer continues.
- Writer leaves system, last reader continues and leaves.
Questions:
- In case of conflict between readers and writers, who gets priority?
- Is the WW necessary in the writer's first if?
- Can OKToRead ever get greater than 1? What about OKToWrite?
- Is the first writer to execute Lock.P() guaranteed to be the first writer to access the data?
Copyright © 2013, 2018 Barton P. Miller
Non-University of Wisconsin students and teachers are welcome to print these notes their personal use. Further reproduction requires permission of the author.