| 當影像存成了數位的檔案後,我們就可對他做一些修改與修補,其中修改(enhancement)的目的是希望這些數位的影像更符合我們的需求,而修補(restoration)的目的是希望影像能夠恢復他本來的風貌,這可能是因為有些物品、繪畫或是手稿可能太過古老,以致影像變得相當不清晰,或者也可能因為攝影的工具的不良,而造成影像的缺陷,這些的希望經由修補的過程而使影像回復他原本的風貌。 基本上,修改與修補的技術是很相近的,所用的方法大致都是希望藉由二維影像中某一個色點(pixel)他四周為的色點,來決定這個點應該有的顏色,通常我們把這個過程稱為
Filtering。透過 Filtering 的技術,大致而言我們可以把影像修改成我們希望的樣子,例如:把影像變得比較模糊或是比較銳利(sharpen),也可以把影像的對比調的更清晰,還可以把影像中物件的輪廓找出來﹍﹍等等。
就影像的修補(restoration)而言,我們是假設一張完美的影像,經過了某種形式的
filtering 之後,再加上一些雜訊(noise),最後變成了現在需要被修補的影像。而影像修補的技術,就是想辦法去猜測那是什麼形式的的
filtering 然後透過
inverse filtering 將影像還原。至於雜訊的部份,應為他的產生是很隨機的,故沒有什麼好方法可以將它去除。可想而知,這樣的修補所能達到的效果是相當有限的,若沒有專家的知識,是很難將影像回復到原本的風貌,所以以現在的技術程度而言,影像修補通常是由專家和電腦一起合力來完成。
※註(1):為了說名的方便,以下的技術都是針對灰階的影像來做說明。
※註(2):所有的數位影像都是二維的不連續函數,但為了說明的方便,我們常常先用假設他是連續的,找出它的特性,之後再把公式轉換成不連續的形式。
|
◎Image Enhancement
Notation:
- f(x):
image, a 2D discrete function. F(x) is its
Fourier transform.
- h(x):
some 2D discrete function (maybe a filter) . H(x)
is its Fourier transform.
- g(x):
image after processing. G(x) is its Fourier
transform.
- * :
convolution operation. (It is the bridge between
Spatial and Frequency domain method)
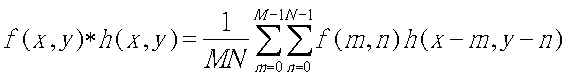
Classification:
- Spatial Domain
Method
- Frequency Domain
Method (Fourier transform)
Motivation:
- Spatial Domain
mothod:
Use
the neighborhood of (x,y) to determine f(x,y)
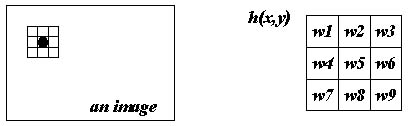
This example is
make use the 8 neighbors to determine the central
pixel. The method to determine could be a
weighted sum of the 3x3 pixels, where the weight
w1...w9 will determine which enhancement to
perform.
- Fourier Domain
method:
1.
Use high frequency to sharpen images.
2. Use low
frequency to blur images.
Point processing:
This method
does not use any neighbor to enhance the image. It is
just a functoion, which map one color to another one
for each color. Although this method is so easy, it
help a lot to make images clear.
- Intensity
transformation:
Example:
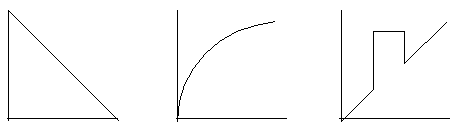
x-axis : original
color y-axis
: new color
We can get a new
image by applying these function to the original
pixels. For example, the first function will
produce a inverse image (black to white and white
to black). The second function will make a dark
picture bright. The third function will emphasis
a special range of colors.
- Histogram
processing:
Histogram
is used to represent "what percentage does a
color have in the image." For example :

x-axis : the
colors in the image y-axis : the probability
the color occurs in the image.
- Histogram
equalization :
This is a kind of
historgram processing to make low-contrast image
high-contrast.

- Image Subtraction:
Subtracting a special
image to make the image more desired.
g(x,y)=f(x,y)-h(x,y)
- Image Averaging:
Averaging a lot of noisy
images which have the same content will delete
the noise.
Spatial Filtering :
Use the neighbors of
some pixel to determine the pixel. For example:

Derivative filters
will find the edge of an object.

Examples :
Original image :

Its histogram of
luminance :

Its histogram of Red
:
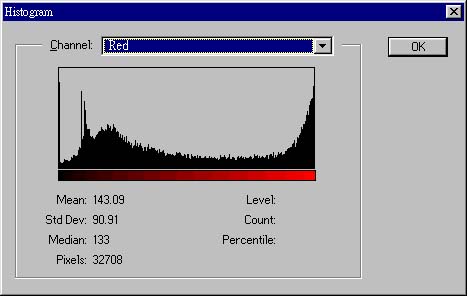
Its histogram or
Green:
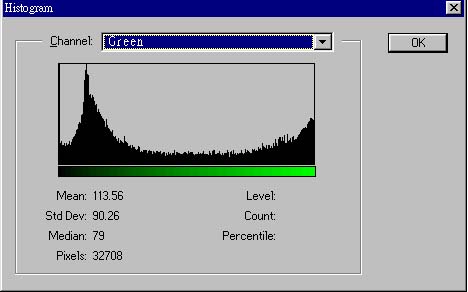
Its histogram of
Blue:

After lowpass
fitlering:

After highpass
filtering:

After Sobel
(Derivative) filtering:
 
merge the above
pictures result edges of object:

Frequency Domain
Enhancement :
- Motivation:
Edges , sharp
transitions and other abrupt changes in gray
levels are associated with high-frequency
components.To sharpen: emphasize high-frequency
components.To blur: emphasize low-frequency
components.
Equation: G(u,v)
= H(u,v)F(u,v)
G(u,v) is the new
image, F(u,v) is the original image, H(u,v) is
the filter.
- Lowpass
filtering:
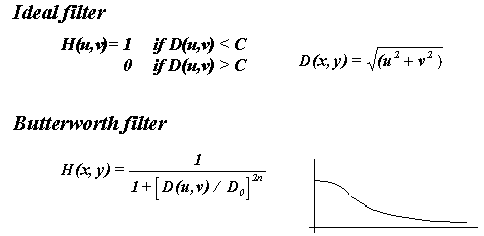
- Highpass
filtering:
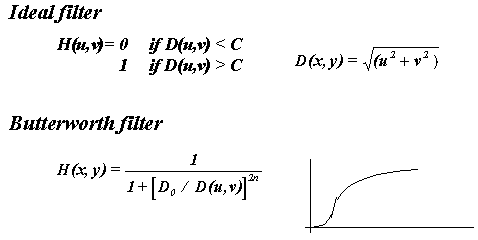
- Frequency
domain method vs. Spatial domain method:


◎Image Restoration
Goal:
- Restore the damaged
originals:
- Restore the damaged image
because of imperfect acquisition: noise, quantization or
geometric transformations.
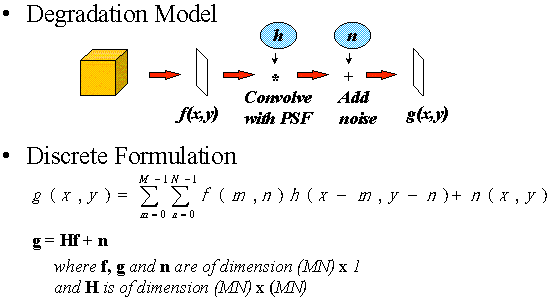
Degradation
Model:
g(x,y)=H[f(x,y)]+n(x,y)
where g(x,y)
is the damaged image, f(x,y) is the perfect image,
n(x,y) is a random noise function, H is some
transformation operation.
Assumption:
H is linear and position invariant.
- H[mf(x.y)+ng(x,y)]=mH[f(x,y)]+nH[g(x,y)]
- H[
f(x-a,y-b) ]=H[f](x-a,y-b)
Point
Spread Function:
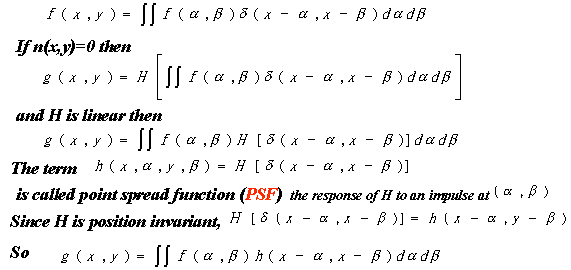
Methods:
- Inverse
filtering:
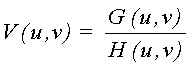
1.
Compute the 2D FFT of image g, called G.
2. Compute the 2D FFT of PSF h, called H.
3. Compute the new image V(u,v)=G(u,v)/H(u,v).
4. Compute the inverse FFT of V.
- other
methods:

|
![]()
![]()
