Examples
Command Window example
Calculate the value of
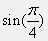
Type the following in the Command Window and press the
Enterafter each command statement.>> sin(pi/4)
You should see the value
0.7071which represents the value of the sine of a 45 degree angle. Notice that thesinfunction requires angles to be entered in radians, not degrees and that the value of is entered by typing the predefined variable name
is entered by typing the predefined variable name pi.You can evaluate the value of other functions in the same way. Just type in the function's name and the input arguments to the function enclosed in parentheses and press
Enter. You can also see the value ofpithat has been pre-defined by Matlab. Just type thepiin the Command Window and pressEnter.Command History example
Click on the command
sin(pi/4)in the Command History window.Note that the expression and its result value are shown in the Command Window.
Here are three other ways to use the Command History:
- Double-click to select and execute commands directly.
- Click and drag the command to the Command Window.
- Copy and paste from the Command History window to the Command Window.
View the Workspace window
Click on the tab labelled Workspace to see this window.
You should see one variable named
answith the value0.07071that was the result ofsin(pi/4).For our purposes, the Command Window and a file Editor window (not open yet) will be most useful until we start writing more complex program code. It is not necessary to close the other windows, but you can close any window that you're not using by clicking on the
 in the upper right hand corner of the window frame that you wish to close. To reopen the window,
use the
in the upper right hand corner of the window frame that you wish to close. To reopen the window,
use the Desktopmenu and select the window that you wish to show on your desktop.Create an examples directory.
Create a new directory named
examplesin thecs310directory that you created in the Topic Discussion section. You can use this directory to store files that you create while working on examples and exercises.Use this widget to change the current directory.

Having a separate directory to store all of your practice work will make it easier for you to find the work you do for Examples and Exercises. It is also a good idea to create a new directory for each homework assignment.
Clear all currently assigned variables.
Type
clearin the Command Window to clear all variables from the Workspace window before starting new problems. Check the Workspace window to see that your variables have been removed after executing theclearcommand from the Command Window.Use the
clearcommand to avoid the situation where variable data from earlier problems is accidentally used and thus interferes with the results of a new problem.Close the Command History window.
Click the small
 and select Close to close the Command History window.
and select Close to close the Command History window.Note that the other windows expand to fill the space.
Reopen the Command History window.
Select
Layout->Command History->Docked(orPopup) from the menu to reopen the Command History window.Open the Editor window
Here are several ways:
- Click the
New m-filebutton. - Select
File -> New -> M-filefrom the menu. - Select
File -> Openfrom the menu and choose the file you wish to open from the directory.
Once the Editor window is open, you may wish to add it to your desktop layout. This is known as docking a window. To dock your Editor window, select
Desktop -> Dock Editorfrom the menu.- Click the
- Type
help sinin the command window and press Enter.Note that there are multiple ways to call thesinfunction. - Type
helpbrowserin the command window and press Enter.Note that a new window is created that allows you to search the entire help system.