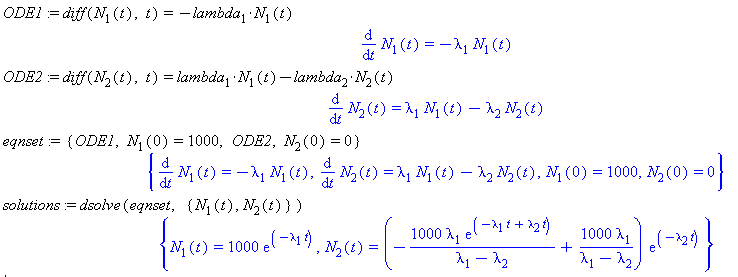Radioactive isotopes decay according to a linear first order ODE that produces an exponential solution. If the daughter
product of the decay process also undergoes radioactive decay, then its population is determined by a second linear first
order ODE that is coupled to the first ODE as shown below. Note that the decay rate
that reduces the number of
serves as a positive contribution to the production of the daughter isotope
in the second equation. In this way, decay chains of radioactive isotopes are mathematically modeled as coupled linear first
order ODEs.
Use the initial conditions:
at t=0 is 1000 and
at t=0 is 0.