"a" is declared

"b" is declared
System.out.println(a);
with the values "first", 0, and 0. Then,
object reference variable a is assigned
to the object.

System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
the value of object referece variable a,
which is the object to which it points.
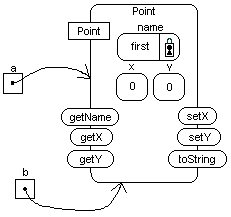
Point first is located at (0,0).
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
object to which object reference variable
a points.
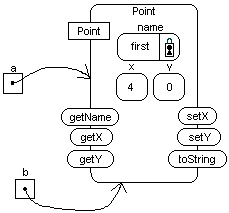
Point first is located at(4,0).
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
object to which object reference variable
b points.+
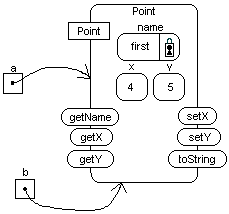
Point first is located at(4,5).
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
with the values "second", -3, and -8. Then,
object reference variable a is assigned to
the object.
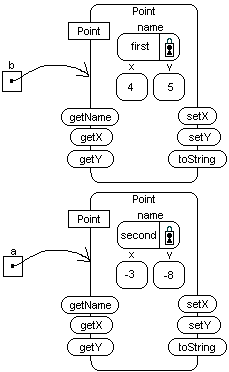
Point first is located at(4,5).
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
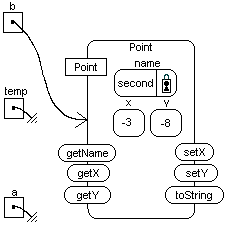
System.out.println(temp);
"temp" is declared and assigned the value
of object reference variable a;

Point first is located at(4,5).
Point second is located at(-3,-8).
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(temp);
value of object reference b.
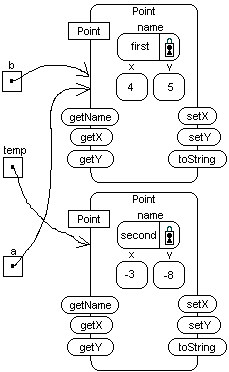
Point first is located at(4,5).
Point second is located at(-3,-8).
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(temp);
value of object reference temp.
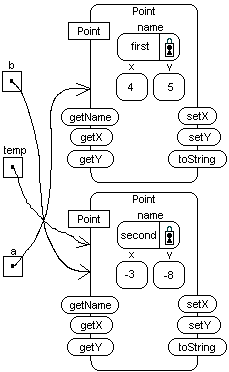
Point second is located at(-3,-8).
Point second is located at(-3,-8).
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
the value of null.

Point second is located at(-3,-8).
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
called on the object that object
reference variable b points to, is
called on the object that object
reference variable a points to.

Point second is located at(-3,-8).
System.out.println(b);
assigned the value of object
reference variable temp.
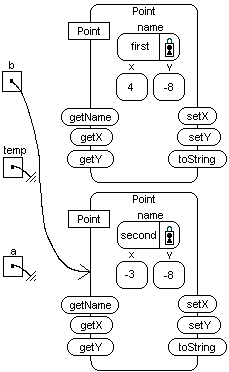
no object reference variables point,
that object will be deallocated
during garbage collection, and no
more object reference variable may
point to it.