 |
 |
Ground Truth |
one of 100 noisy images, noise std = 20, PSNR=22.2231 dB |
Single-Image Deblurring verus Multi-Image Denoising on 'Blackboard' synthetic dataset
(for all figures, noise standard deviation in the range [0-255])
 |
 |
Ground Truth |
one of 100 noisy images, noise std = 20, PSNR=22.2231 dB |
The following figures show a comparison between Single-Image Deblurring and Multi-Image Denoising for 4 different synthetic kernels.
The performance of deblurring depends on the kernel and the prior. The performance of multi-image denoising with a weak prior is higher than that for single-image deblurring method with either a weak or stronger prior.
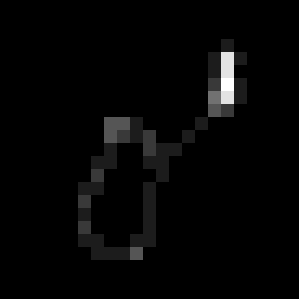 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
synthetic kernel #1 |
blurry image |
deblurring using weak prior, PSNR=24.5598 dB |
deblurring using strong prior, PSNR=30.6238 dB |
denoising result using weak prior, PSNR=41.9675 dB |
ground truth |
 |
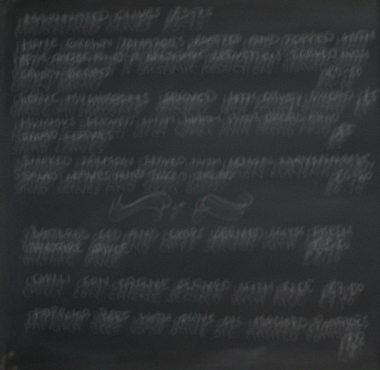 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
synthetic kernel #2 |
blurry image |
deblurring using weak prior, PSNR=24.4779 dB |
deblurring using strong prior, PSNR=30.2877 dB |
denoising result using weak prior, PSNR=41.9675 dB |
ground truth |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
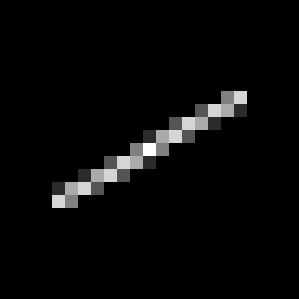
synthetic kernel #3 |
blurry image |
deblurring using weak prior, PSNR=25.6387 dB |
deblurring using strong prior, PSNR=31.0511 dB |
denoising result using weak prior, PSNR=41.9675 dB |
ground truth |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
synthetic kernel #4 |
blurry image |
deblurring using weak prior, PSNR=23.7985 dB |
deblurring using strong prior, PSNR=29.3698 dB |
denoising result using weak prior, PSNR=41.9675 dB |
ground truth |
The two priors used the above comparison:
The weak prior is the ground truth image corrupted with synthetic Gaussian noise of std deviation 40. The strong prior is the denoised result of a state-of-the-art single image denoising method CBM3D.
 |
 |
Weak Prior |
Strong Prior |