Adding cache to the configuration script¶
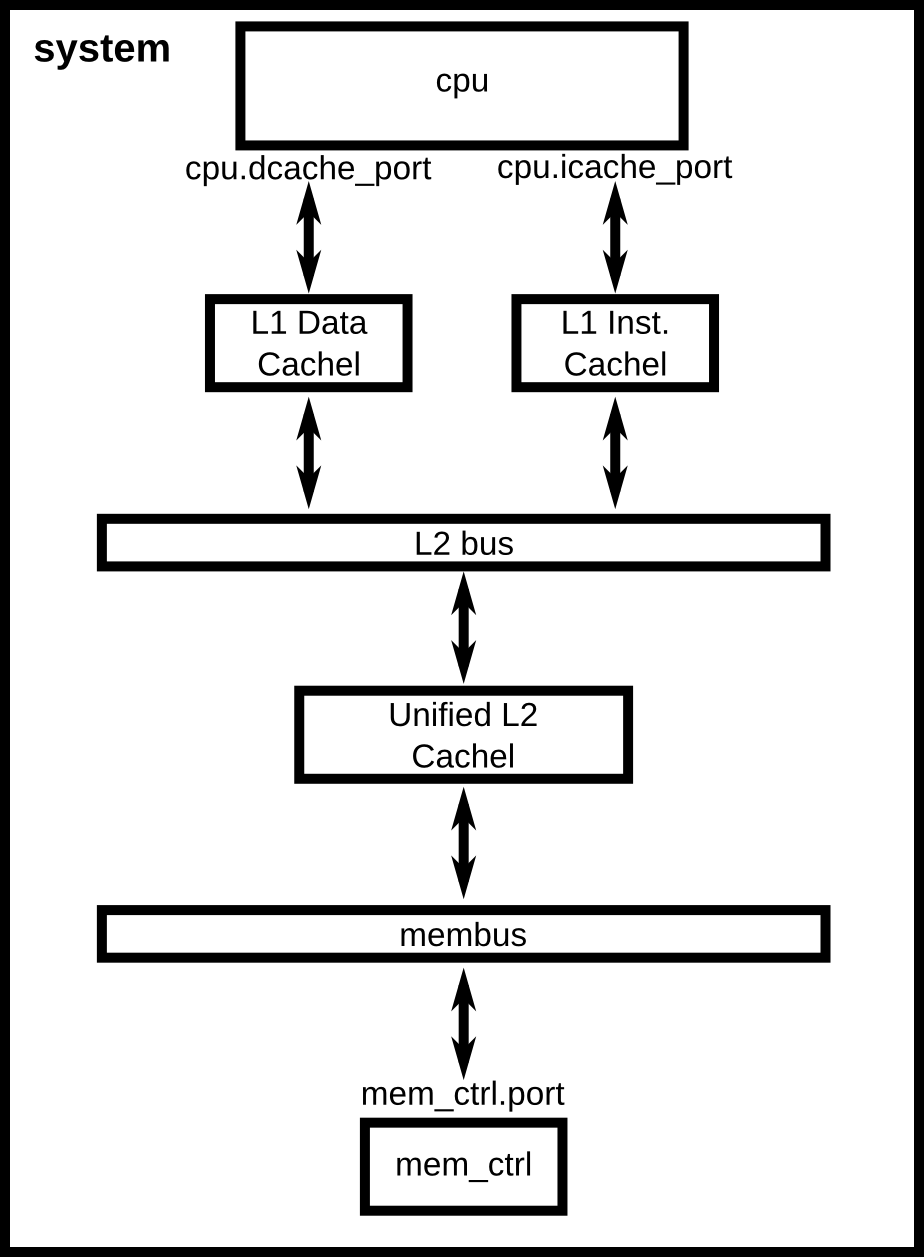
Using the previous configuration script as a starting point, this chapter will walk through a more complex configuration. We will add a cache hierarchy to the system as shown in the figure below. Additionally, this chapter will cover understanding the gem5 statistics output and adding command line parameters to your scripts.
Creating cache objects¶
We are going to use the classic caches, instead of ruby, since we are modeling a single CPU system and we don’t care about modeling cache coherence. We will extend the Cache SimObject and configure it for our system. First, we must understand the parameters that are used to configure Cache objects.
Todo
We should add links to SimObjects like Cache that point to the doxygen on gem5’s site.
Cache¶
The Cache SimObject declaration can be found in src/mem/cache/Cache.py. This Python file defines the parameters which you can set of the SimObject. Under the hood, when the SimObject is instantiated these parameters are passed to the C++ implementation of the object. The Cache SimObject inherits from the BaseCache object shown below.
from m5.params import *
from m5.proxy import *
from MemObject import MemObject
from Prefetcher import BasePrefetcher
from Tags import *
class BaseCache(MemObject):
type = 'BaseCache'
abstract = True
cxx_header = "mem/cache/base.hh"
size = Param.MemorySize("Capacity")
assoc = Param.Unsigned("Associativity")
tag_latency = Param.Cycles("Tag lookup latency")
data_latency = Param.Cycles("Data access latency")
response_latency = Param.Cycles("Latency for the return path on a miss");
max_miss_count = Param.Counter(0,
"Number of misses to handle before calling exit")
mshrs = Param.Unsigned("Number of MSHRs (max outstanding requests)")
demand_mshr_reserve = Param.Unsigned(1, "MSHRs reserved for demand access")
tgts_per_mshr = Param.Unsigned("Max number of accesses per MSHR")
write_buffers = Param.Unsigned(8, "Number of write buffers")
is_read_only = Param.Bool(False, "Is this cache read only (e.g. inst)")
prefetcher = Param.BasePrefetcher(NULL,"Prefetcher attached to cache")
prefetch_on_access = Param.Bool(False,
"Notify the hardware prefetcher on every access (not just misses)")
tags = Param.BaseTags(LRU(), "Tag store (replacement policy)")
sequential_access = Param.Bool(False,
"Whether to access tags and data sequentially")
cpu_side = SlavePort("Upstream port closer to the CPU and/or device")
mem_side = MasterPort("Downstream port closer to memory")
addr_ranges = VectorParam.AddrRange([AllMemory],
"Address range for the CPU-side port (to allow striping)")
system = Param.System(Parent.any, "System we belong to")
# Enum for cache clusivity, currently mostly inclusive or mostly
# exclusive.
class Clusivity(Enum): vals = ['mostly_incl', 'mostly_excl']
class Cache(BaseCache):
type = 'Cache'
cxx_header = 'mem/cache/cache.hh'
# Control whether this cache should be mostly inclusive or mostly
# exclusive with respect to upstream caches. The behaviour on a
# fill is determined accordingly. For a mostly inclusive cache,
# blocks are allocated on all fill operations. Thus, L1 caches
# should be set as mostly inclusive even if they have no upstream
# caches. In the case of a mostly exclusive cache, fills are not
# allocating unless they came directly from a non-caching source,
# e.g. a table walker. Additionally, on a hit from an upstream
# cache a line is dropped for a mostly exclusive cache.
clusivity = Param.Clusivity('mostly_incl',
"Clusivity with upstream cache")
# Determine if this cache sends out writebacks for clean lines, or
# simply clean evicts. In cases where a downstream cache is mostly
# exclusive with respect to this cache (acting as a victim cache),
# the clean writebacks are essential for performance. In general
# this should be set to True for anything but the last-level
# cache.
writeback_clean = Param.Bool(False, "Writeback clean lines")
Within the BaseCache class, there are a number of parameters. For instance, assoc is an integer parameter. Some parameters, like write_buffers have a default value, 8 in this case. The default parameter is the first argument to Param.*, unless the first argument is a string. The string argument of each of the parameters is a description of what the parameter is (e.g., tag_latency = Param.Cycles("Tag lookup latency") means that the `tag_latency controls “The hit latency for this cache”).
Many of these parameters do not have defaults, so we are required to set these parameters before calling m5.instantiate().
Now, to create caches with specific parameters, we are first going to create a new file, caches.py, in the same directory as simple.py, configs/tutorial. The first step is to import the SimObject(s) we are going to extend in this file.
from m5.objects import Cache
Next, we can treat the BaseCache object just like any other Python class and extend it. We can name the new cache anything we want. Let’s start by making an L1 cache.
class L1Cache(Cache):
assoc = 2
tag_latency = 2
data_latency = 2
response_latency = 2
mshrs = 4
tgts_per_mshr = 20
Here, we are setting some of the parameters of the BaseCache that do not have default values. To see all of the possible configuration options, and to find which are required and which are optional, you have to look at the source code of the SimObject. In this case, we are using BaseCache.
We have extended BaseCache and set most of the parameters that do not have default values in the BaseCache SimObject. Next, let’s two more sub-classes of L1Cache, an L1DCache and L1ICache
class L1ICache(L1Cache):
size = '16kB'
class L1DCache(L1Cache):
size = '64kB'
Let’s also create an L2 cache with some reasonable parameters.
class L2Cache(Cache):
size = '256kB'
assoc = 8
tag_latency = 20
data_latency = 20
response_latency = 20
mshrs = 20
tgts_per_mshr = 12
Now that we have specified all of the necessary parameters required for BaseCache, all we have to do is instantiate our sub-classes and connect the caches to the interconnect. However, connecting lots of objects up to complex interconnects can make configuration files quickly grow and become unreadable. Therefore, let’s first add some helper functions to our sub-classes of Cache. Remember, these are just Python classes, so we can do anything with them that you can do with a Python class.
To the L1 cache let’s add two functions, connectCPU to connect a CPU to the cache and connectBus to connect the cache to a bus. We need to add the following code to the L1Cache class.
def connectCPU(self, cpu):
# need to define this in a base class!
raise NotImplementedError
def connectBus(self, bus):
self.mem_side = bus.slave
Next, we have to define a separate connectCPU function for the instruction and data caches, since the I-cache and D-cache ports have a different names. Our L1ICache and L1DCache classes now become:
class L1ICache(L1Cache):
size = '16kB'
def connectCPU(self, cpu):
self.cpu_side = cpu.icache_port
class L1DCache(L1Cache):
size = '64kB'
def connectCPU(self, cpu):
self.cpu_side = cpu.dcache_port
Finally, let’s add functions to the L2Cache to connect to the memory-side and CPU-side bus, respectively.
def connectCPUSideBus(self, bus):
self.cpu_side = bus.master
def connectMemSideBus(self, bus):
self.mem_side = bus.slave
The complete file can be downloaded here.
Adding caches the simple config file¶
Now, let’s add the caches we just created to the configuration script we created in the last chapter.
First, let’s copy the script to a new name.
cp simple.py two_level.py
First, we need to import the names from the caches.py file into the namespace. We can add the following to the top of the file, as you would with any Python source.
from caches import *
Now, after creating the CPU, let’s create the L1 caches:
system.cpu.icache = L1ICache()
system.cpu.dcache = L1DCache()
And connect the caches to the CPU ports with the helper function we created.
system.cpu.icache.connectCPU(system.cpu)
system.cpu.dcache.connectCPU(system.cpu)
Also, You need to remove the previous lines which connected the cache ports directly to the memory bus.
-system.cpu.icache_port = system.membus.slave
-system.cpu.dcache_port = system.membus.slave
We can’t directly connect the L1 caches to the L2 cache since the L2 cache only expects a single port to connect to it. Therefore, we need to create an L2 bus to connect our L1 caches to the L2 cache. The, we can use our helper function to connect the L1 caches to the L2 bus.
system.l2bus = L2XBar()
system.cpu.icache.connectBus(system.l2bus)
system.cpu.dcache.connectBus(system.l2bus)
Next, we can create out L2 cache and connect it to the L2 bus and the memory bus.
system.l2cache = L2Cache()
system.l2cache.connectCPUSideBus(system.l2bus)
system.l2cache.connectMemSideBus(system.membus)
Everything else in the file stays the same! Now we have a complete configuration with a two-level cache hierarchy. If you run the current file, hello should now finish in 58513000 ticks. The full script can be found here.
Adding parameters to your script¶
When performing experiments with gem5, you don’t want to edit your configuration script every time you want to test the system with different parameters. To get around this, you can add command-line parameters to your gem5 configuration script. Again, because the configuration script is just Python, you can use the Python libraries that support argument parsing. Although optparse is officially deprecated, the configuration scripts that ship with gem5 use it instead of py:mod:argparse since gem5’s minimum Python version is 2.5. To get started using optparse, you can consult the online Python documentation.
To add options to our two-level cache configuration, after importing our caches, let’s add some options.
from optparse import OptionParser
parser = OptionParser()
parser.add_option('--l1i_size', help="L1 instruction cache size")
parser.add_option('--l1d_size', help="L1 data cache size")
parser.add_option('--l2_size', help="Unified L2 cache size")
(options, args) = parser.parse_args()
Now, you can run build/X86/gem5.opt configs/tutorial/two_level_opts.py --help which will display the options you just added.
Next, we need to pass these options onto the caches that we create in the configuration script. To do this, we’ll simple change pass the options into the caches as a parameter to their constructor and add an appropriate constructor, next.
system.cpu.icache = L1ICache(options)
system.cpu.dcache = L1DCache(options)
...
system.l2cache = L2Cache(options)
In caches.py, we need to add constructors (__init__ functions in Python) to each of our classes. Starting with our base L1 cache, we’ll just add an empty constructor since we don’t have any parameters which apply to the base L1 cache. However, we can’t forget to call the super class’s constructor in this case. If the call to the super class constructor is skipped, gem5’s SimObject attribute finding function will fail and the result will be “RuntimeError: maximum recursion depth exceeded” when you try to instantiate the cache object. So, in L1Cache we need to add the following after the static class members.
def __init__(self, options=None):
super(L1Cache, self).__init__()
pass
Next, in the L1ICache, we need to use the option that we created (l1i_size) to set the size. In the following code, there is guards for if options is not passed to the L1ICache constructor and if no option was specified on the command line. In these cases, we’ll just use the default we’ve already specified for the size.
def __init__(self, options=None):
super(L1ICache, self).__init__(options)
if not options or not options.l1i_size:
return
self.size = options.l1i_size
We can use the same code for the L1DCache:
def __init__(self, options=None):
super(L1DCache, self).__init__(options)
if not options or not options.l1d_size:
return
self.size = options.l1d_size
And the unified L2Cache:
def __init__(self, options=None):
super(L2Cache, self).__init__()
if not options or not options.l2_size:
return
self.size = options.l2_size
With these changes, you can now pass the cache sizes into your script from the command line like below.
build/X86/gem5.opt configs/tutorial/two_level_opts.py --l2_size='1MB' --l1d_size='128kB'
gem5 Simulator System. http://gem5.org
gem5 is copyrighted software; use the --copyright option for details.
gem5 compiled Sep 6 2015 14:17:02
gem5 started Sep 6 2015 15:06:51
gem5 executing on galapagos-09.cs.wisc.edu
command line: build/X86/gem5.opt ../tutorial/_static/scripts/part1/two_level_opts.py --l2_size=1MB --l1d_size=128kB
Global frequency set at 1000000000000 ticks per second
warn: DRAM device capacity (8192 Mbytes) does not match the address range assigned (512 Mbytes)
0: system.remote_gdb.listener: listening for remote gdb #0 on port 7000
Beginning simulation!
info: Entering event queue @ 0. Starting simulation...
Hello world!
Exiting @ tick 56742000 because target called exit()
The updated configuration script can be downloaded here and the updated cache file can be downloaded here.