Examples
- Assign numeric values to each of the following variable names:
- wallHeight
- 1stChoice
- sumOfAll
>> wallHeight = 4.566 wallHeight = 4.5660 >> 1stChoice = 3 ??? 1stChoice = 3 | Error: Unexpected MATLAB expression. >> sumOfAll = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 sumOfAll = 15 >>Notice the error that occurs when you start a variable name with a digit. This is not allowed in Matlab.
- Enter the following at the Command Window. What happens? Why?
>> q+3 = p
>> q+3 = p ??? q+3 = p | Error: The expression to the left of the equals sign is not a valid target for an assignment. >>This error is generated because it doesn't make sense to assign a value (
p) to an expression (q+3). You can only assign values to single variable names. - What happens when you enter a value like 2,929 as
2,929?Try this!
A = 2,929
>> A = 2,929 A = 2 ans = 929 >>
Carefully view the output produced in the Command Window to see that two variables were given values.
Agets the value2andansgets the value929. What if you used two commas? - Assign the value 70 to the variable
Fand write a statement that evaluates this formula and assigns the result to the variableC.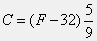
>> F = 70 F = 70 >> C = (F-32)*5/9 C = 21.1111 >>
The formula given converts a Fahrenheit temperature into the equivalent Celsius temperature.
- Reassign
Fto the value 212. Check the Workspace window to see if the value ofCchanged. Why did or didn't the value ofCchange?The value of
Cdoes not change. You would have to also reexecute theC = (F-32)*5/9statement.