Examples
- Copy these files to your current working directory: fff.m and example1.m
- Set a break point at line 2 in the
example1.mfile. - Click the run button from the editor window.
The editor window should now look like this.
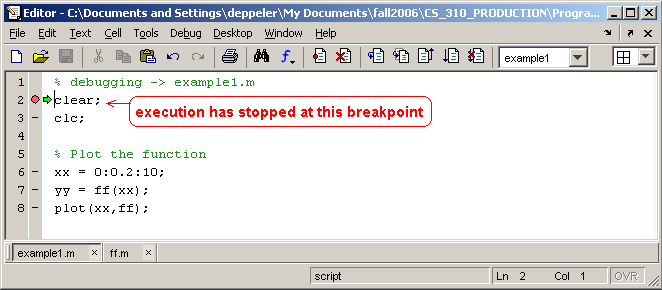
Notice that the debugger operations are all available. First, we will simply step through this script one line at a time. Dock the editor window and make sure that the workspace and command windows are showing before continuing with this example.
Click on the Step button and watch what happens in the workspace window. After executing the
clearcommand, the workspace is cleared of all variables.Click on the Step button again and see that the
clccommand clears the command window.Click on the Step button again to execute the statement that creates the
xxvector. View the results in the workspace window.The editor looks like this now.
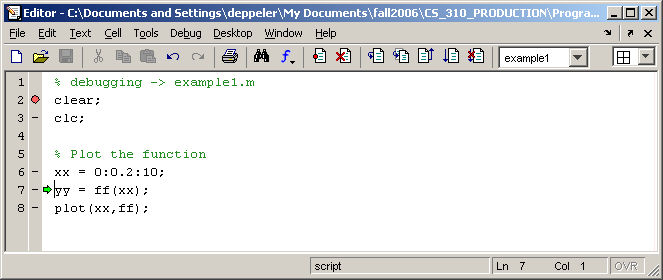
Click on the Step button to execute line 7, the line that creates the
yyvector by calling thefffunction. The debugger stops and an error is displayed in the command window. The next screen shot shows the error that occurs and is shown in the command window.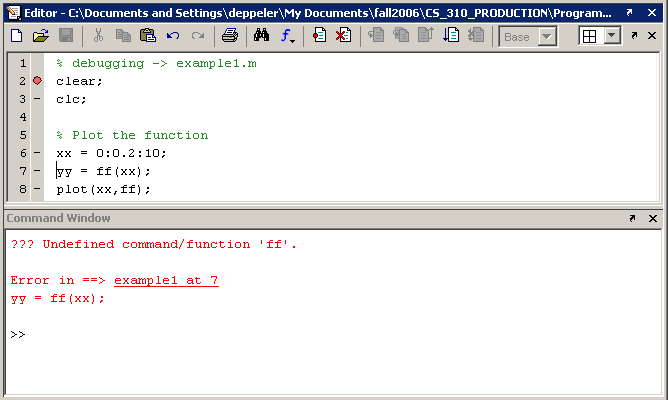
- Fix the error by typing the correct name of the function
fff. - Remove the earlier breakpoint (at line 2) by clicking on the red dot.
- Set a new breakpoint at line 7 since we know the earlier lines are working.
- Click the Run button to start the program again.
The editor window should now look like this with the execution stopped at the breakpoint on line 7.
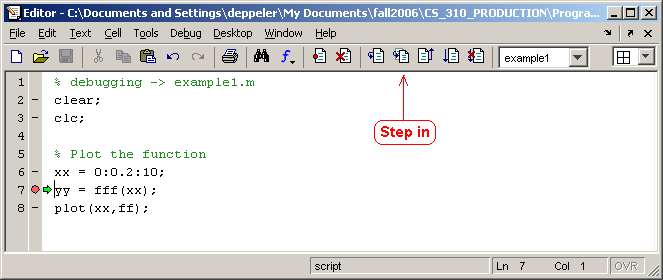
Click on the Step in button instead of the Step button. Notice that the file
fff.mis now showing in the editor window and the green execution arrow is indicating the first line of the function.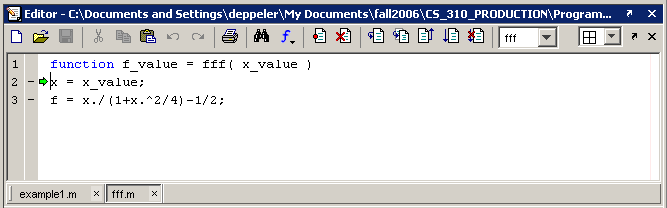
Click the Step button to execute the first line of the function. This line creates a copy of the input value with a more convenient name.
Click the Step button to execute the last line of the function and view the results. Notice the green indicator arrow at the end of the function.
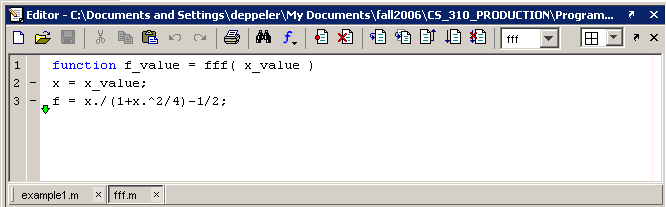
Click the Step button to execute the last line of the function and view the results. Notice the errors that occur when the function returns. The main problem is listed first. This error indicates that the named return value,
f_value, of the function was not assigned to.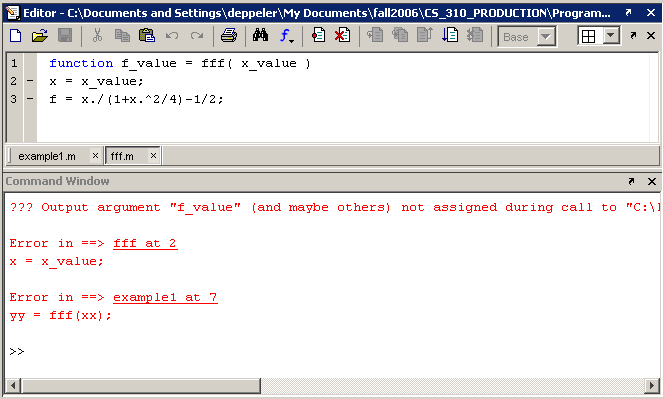
- Fix the error by changing line 3 of the function
fff.mto:f_value = x./(1+x.^2/4)-1/2;
- Save the
fff.mfile. - Click on the
example1.mfile in the editor window. - Click on the Run button to start executing the program again.
- Click on the Step in button to enter the function again.
- Click on the Step button to execute each line of the function.
- Click on the Step button to execute the return from the function.
Control returns successfully to the
example1.mprogram script. View the workspace window to see that the variableyyhas been created successfully.Click on the Step button to execute the last line of the program.
One more error occurs.
- Change
fftoyyto fix this last error. - Save the file.
- Remove the breakpoint at line 7
- Set a breakpoint at line 8
- Click on the Run button to start the program again.
Click on the Step button to execute the
plotcommand and see the plot of the function namedfff.This tutorial has walked you through some common steps for debugging a program. Debugging in this way is most effective when you have found the few lines in which the error is occurring.If you have no idea where to set a breakpoint to get started debugging, it is often good to remove any output suppression characters (
;) and run the program. This will allow the programmer to see where the output is not as expected. Set breakpoints a few lines before the incorrect output occurs and then step through each line of the program's execution path from that point on.