|
|
|
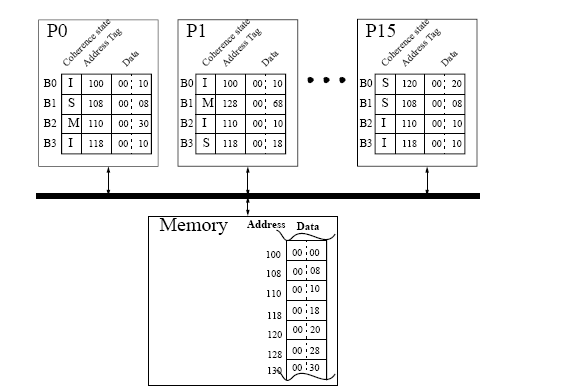
Homework 5 // Due at review session, Monday December 15thProblem 1 (30 points)The simple, bus-based multiprocessor illustrated below represents a commonly-implemented symmetric shared-memory architecture. Each processor has a single, private cache with coherence maintained using the snooping coherence protocol of Figure 4.7. Each cache is direct-mapped, with four blocks each holding two words. To simplify the illustration, the cache address tag contains the full address and each word shows only two hex characters, with the least significant word on the right. The coherence states are denoted M, S, and I for Modified, Shared, and Invalid.
For each subproblem below, assume the initial cache and memory state as illustrated in the figure. Each subproblem specifies a sequence of one or more CPU operations of the form: P#: <op> <address> [ <-- <value> ] Where P# designates the CPU (e.g., P0), <op> is the CPU operation (e.g., read or write), <address> denotes the memory address, and <value> indicates the new word to be assigned on a write operation. What is the final state (i.e., coherence state, tags, and data) of the caches and memory after the given sequence of CPU operations has completed? Show only the blocks that change, e.g., P0.B0: (I, 120, 00 01) indicates that CPU P0ís block B0 has the final state of I, tag of 120, and data words 00 and 01. Also, what value is returned by each read operation?
Problem 2 (20 points)
H&P Problem 4.3 (4th edition)
Problem 3 (20 points)H&P Problem 6.1 (4th edition) Problem 4 (30 points)H&P Problem 6.3 (4th edition) |