Contents
- Introduction
- Hard Code Word
- Results
- Locality-constrained Linear
- Results
- Grid Search
- Sequential Hierarchy Classifier
- Manually assigned clusters
- Results
- Clusters from K-means
- Results
- Other Dataset Evaluation
- Birds
- Butterflies
- Other Experiments
- Results
- Scene Datasets
- Code
- Git Logs
- References
|
Locality-constrained Linear Coding (LLC)
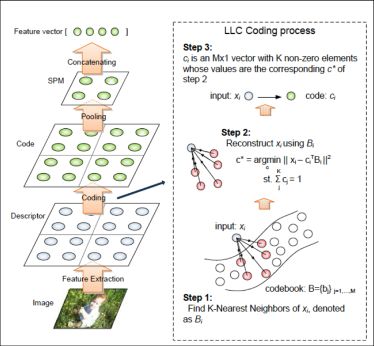 We also experimented with the Locality-constrained Linear Coding method which involves
using the spatial pyramid matching scheme but with a soft codeword assignment. LLC consists of
the following modifications to the original spatial pyramid code.
We also experimented with the Locality-constrained Linear Coding method which involves
using the spatial pyramid matching scheme but with a soft codeword assignment. LLC consists of
the following modifications to the original spatial pyramid code.
- Rather than assigning each SIFT descriptor to just 1 of the M clusters,
find the k-nearest neighbors (out of the M clusters) for each of the SIFT descriptors
in each image. We chose to use k = 5.
- Then, use those nearest neighbors to reconstruct the feature x to be an M x 1 vector where
that vector has k non zero values. These k values will be normalized according to the relevant
clusters' distances to the particular SIFT descriptor.
- Rather than using a sum pooling method and concatenating all of the features for
each sub region in the spatial pyramid scheme, LLC uses a max pooling method. This
involves taking the maximum c value (cluster assignment value) to construct the
c vector for each pyramid level, and then normalizing it by the length of that c vector.
In using the LLC method, we found good results with the benefit of better computational speed!
|